More than ½ the worlds population now use the Internet, and it is predicted that the number of connected devices will reach a staggering 125 billion within the next 10 years. This surely would mean also that the Cyber Security of all devices has improved along with it, right?
The answer is yes, however, the number of reporting cyber-attacks has also grown to near 780 million known incidents in the last 10 years.
There are many types of infringement, but top of most lists and the one that currently raises the most concern is ‘Malware’.
What is Malware?
Malware– is any piece of software that was written with the intent of doing harm. Different types of malware include; viruses, ransomware, trojans and spyware. Usually a computer becomes infected when opening an attachment. Malicious code is often contained within emails, attachments, downloaded files, web pages, etc.
Other common security threats:
Advanced Persistent Threats – Involves a cyber-criminal gaining un-authorised access to a network and remaining undetected for an extended period of time. Malware and Phishing techniques are used to gain initial entry. Following the initial access activities include setting an additional back door access to the network, information is usually the target for theft.
Data Ex filtration – Usually associated with a cyber-criminal targeting and copying specific types of valuable data. The criminal more often gains initial access via a weak or leaked password, and then installs a means of remote access to carryout the theft.
Unauthorised Network Access – There are numerous ways of accessing an unsecured network, or a network you think is secure. Surveillance techniques will highlight insecurities, open ports, mis-configured access software, and weak password security are common opportunities.
Man-in-the-middle attack – is an attack where the attacker secretly relays and or alters the communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other. Example being eavesdropping, in which the attacker makes independent connections with the victims and relays messages between them to make them believe they are talking directly to each other over a private connection. Unsecured Wireless Access Points, especially those used in a public space attract this type of cyber crime activity.
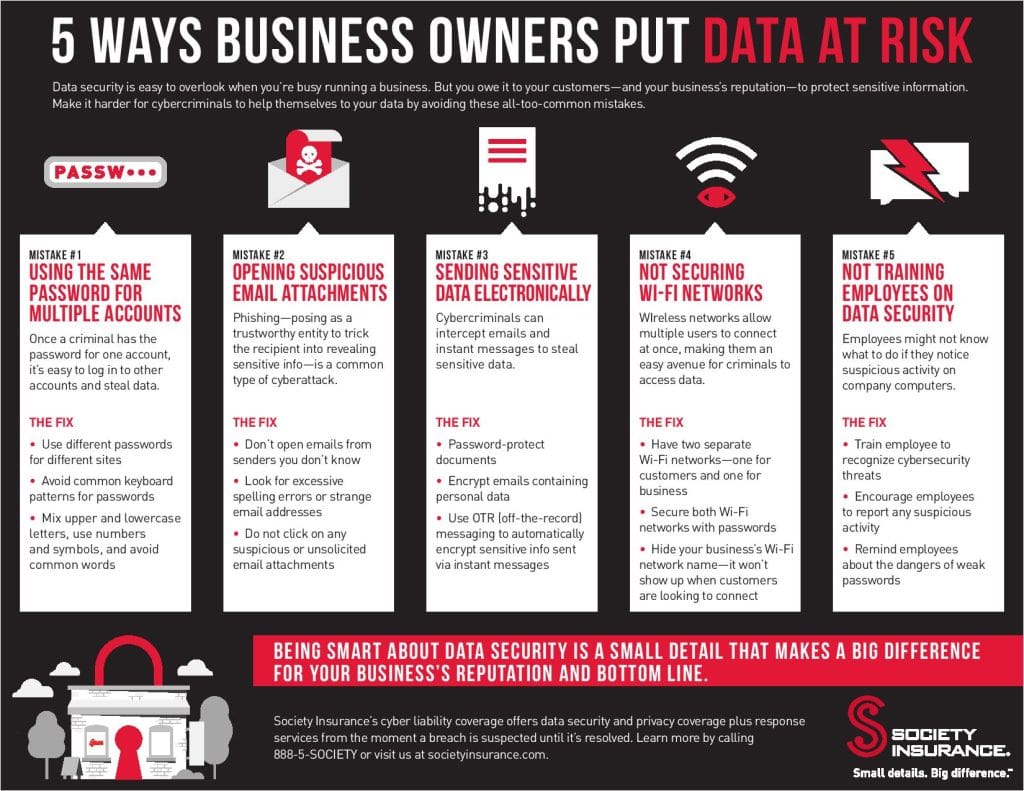
Human Error – 80% of Reported Breaches in 2017/2018 were the result of human or process error. Poor user education, password control and granting excessive privileges to users were common areas for concern.
The image below outlines how users can accidentally cause cyber threats.
Over the next 3 months, each week I will address each point in detail, and together they will build to create an action plan that will drive down the Cyber Security threat.
At Solutions 4 IT, we specialise in looking at your network. Specifically, how old your devices are, the cyber security measurements put into place and the physical protection on-site. If you are interested in looking into our services, be sure to click this link.